PRODUCTSMedical Simulation
Emergency Medical Simulation
- Specification
- Description
- Notes
Material verified by SGS: Heavy metal-free, plasticizer-free, no PAHs.
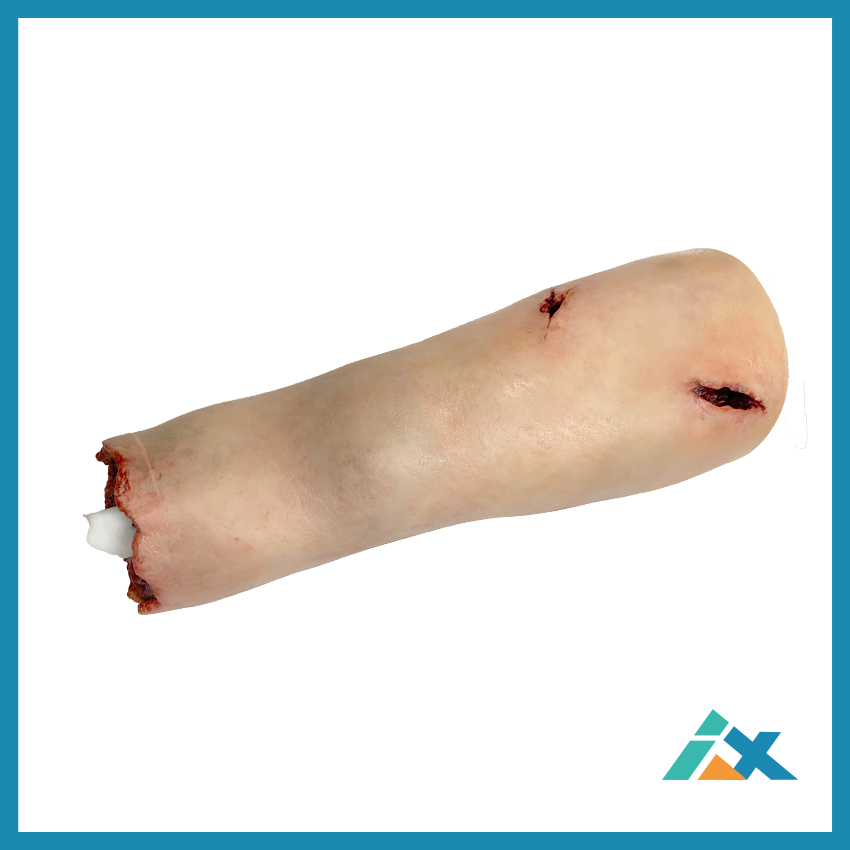
It comes with three types of simulated injuries to practice tourniquet hemostasis, packing hemostasis, and gauze compression hemostasis, with bleeding simulated via a gravity drainage bag.
- The skin is made of high-quality silicone material, simulating human skin.
- Highly realistic silicone Thigh .
- Flow control through gravity drainage bag (2L).
- Common simulated wounds (cuts, gunshot wounds, deep wounds).
- For a more realistic effect, use red liquid to simulate bleeding.
- Practice direct pressure.
- Practice tourniquet application.
- Practice wound packing.
- Each wound bleeds independently.
- The material is durable and can be cleaned with soap and water.
Reusable.
-
Receive your order in 2 -4 weeks.
-
Shipped By Dhl, UPS or FedEx in Anonymous Package. Tracking number included.
-
Those specified nationalities are subject to the extra tax.
- Carefully read the product description and specifications to ensure the item meets your needs and expectations.
- Inquire about the actual price, shipping fees, and any additional charges to avoid discrepancies or overpayments.
- Check the product’s stock availability to confirm it is in stock or can be promptly replenished, preventing issues like out-of-stock notifications or shipping delays after ordering.
- Thoroughly review the website’s return and exchange policy before purchasing to ensure you have a fair resolution in case of any issues with the product.
- Choose secure and reliable payment methods, such as online banking, to guarantee a safe payment process.
- Keep your order number and payment receipt safely after purchase for future reference and order verification.
Thigh Hemorrhage Control Training Model (Three Injury Types):
1.Introduction:
In emergency situations, hemorrhage control is an extremely important skill and one that every responder must possess. During training, rescuers must learn the appropriate methods to stop bleeding, including techniques for direct pressure, wound packing, and the proper use of tourniquets. When someone is injured in an accident or disaster, effective bleeding control can save lives.
Direct pressure, tourniquet application, and wound packing are essential techniques. Through hands-on practice and repeated training, responders can develop the ability to make the right decisions during real-life emergencies.
2.Functionality:

- Direct Pressure Training:
When practicing direct pressure on the arm model, the trainee must locate the injury site and apply firm pressure above the wound using hemostatic gauze to help slow the bleeding. This technique requires a controlled amount of force and pressure, as excessive force can cause further injury. Therefore, rescuers must learn to manage the pressure appropriately to effectively stop the bleeding without causing additional harm. - Tourniquet Training:
This thigh model simulates amputation (with vascular retraction and rebound) as well as obese patients. Therefore, the tourniquet must be applied to the red-marked area (the proximal side of the wound) to replicate the most effective position for hemorrhage control in real-life scenarios. The dotted area in the picture is a special design feature to simulate situations where a single tourniquet is insufficient to stop bleeding. When the tourniquet is applied at the dotted position, it will not effectively occlude arterial blood flow, resulting in continued bleeding. In such cases, trainees must identify the cause of failure and immediately apply a second tourniquet to the red-marked area to achieve effective hemorrhage control. This design effectively trains trainees to adapt to real-world changes, improving both decision-making and response capabilities. Note: Proper application techniques must be learned to achieve effective hemorrhage control while avoiding further injury.This thigh model simulates amputation (with vascular retraction and rebound) as well as obese patients. Therefore, the tourniquet must be applied to the red-marked area (the proximal side of the wound) to replicate the most effective position for hemorrhage control in real-life scenarios. The dotted area in the picture is a special design feature to simulate situations where a single tourniquet is insufficient to stop bleeding. When the tourniquet is applied at the dotted position, it will not effectively occlude arterial blood flow, resulting in continued bleeding. In such cases, trainees must identify the cause of failure and immediately apply a second tourniquet to the red-marked area to achieve effective hemorrhage control. This design effectively trains trainees to adapt to real-world changes, improving both decision-making and response capabilities. Note: Proper application techniques must be learned to achieve effective hemorrhage control while avoiding further injury.This thigh model simulates amputation (with vascular retraction and rebound) as well as obese patients. Therefore, the tourniquet must be applied to the red-marked area (the proximal side of the wound) to replicate the most effective position for hemorrhage control in real-life scenarios. The dotted area in the picture is a special design feature to simulate situations where a single tourniquet is insufficient to stop bleeding. When the tourniquet is applied at the dotted position, it will not effectively occlude arterial blood flow, resulting in continued bleeding. In such cases, trainees must identify the cause of failure and immediately apply a second tourniquet to the red-marked area to achieve effective hemorrhage control. This design effectively trains trainees to adapt to real-world changes, improving both decision-making and response capabilities. Note: Proper application techniques must be learned to achieve effective hemorrhage control while avoiding further injury. - Wound Packing Training:
For deeper or larger wounds, or wounds located at junctional areas of the torso, wound packing is a viable technique. It is recommended to use gauze with hemostatic agents; however, for model training, regular continuous gauze can be used. First, wrap several turns of gauze around the insertion finger to protect it from sharp fragments, then pack the gauze into the wound in the direction toward the heart. Once the wound is filled, apply direct pressure above the wound to help stop the bleeding. This method, which is incorporated into TECC/TCCC training courses, requires repeated practice to effectively manage various injuries and minimize blood loss.
When employing any first aid techniques, proper training is essential, and one must remain vigilant about potential risks and complications.
3.Advantages of Thigh Hemorrhage Control Training Model :
-
Realistic Training Environment : Thigh Hemorrhage Control Training Model are designed to simulate real human anatomy and bleeding scenarios, allowing trainees to practice in a controlled, yet realistic environment. This realistic simulation enhances the trainee’s ability to perform effective hemorrhage control in real-life situations.
Versatile Wound Types : Thigh Hemorrhage Control Training Model often come with various types of wounds, such as lacerations, gunshot wounds, and eviscerations. This variety allows trainees to practice different hemorrhage control techniques, including direct pressure, tourniquet application, and wound packing.
Repeated Practice : The durable materials used in Thigh Hemorrhage Control Training Model enable repeated practice without degrading the quality of the simulation. Trainees can repeatedly apply and refine their techniques, leading to greater proficiency.
Safety and Ethical Training :Thigh Hemorrhage Control Training Model provide a safe and ethical way to practice life-saving techniques. Training on live subjects can be painful and impractical, whereas simulators offer a humane alternative.
Immediate Feedback and Learning : Many Thigh Hemorrhage Control Training Model come with features that provide immediate feedback, such as realistic bleeding responses to applied techniques. This instant feedback helps trainees quickly understand the effectiveness of their interventions.
4.The contents of the product:
- Silicone Professional Thigh Hemorrhage Control Training (Three Types of Trauma: Tourniquet Application, direct pressure, Wound Packing).
- Product packaging.
- Gravity drainage bag (2 liters).
- Tourniquet is not included in the supply range.